Introduction
Project documentation is a crucial aspect of successful project management. It serves as a roadmap, a communication tool, a reference guide, and a historical record all at once.
Without proper documentation, projects can easily become disorganised, inefficient, and prone to miscommunication. Whether you’re managing a small project or a complex initiative, well-organised documentation is the compass that guides your journey. From planning and execution to monitoring and closure, every phase of a project relies on clear, comprehensive records.
Here are the best practices for creating and maintaining effective project documentation.
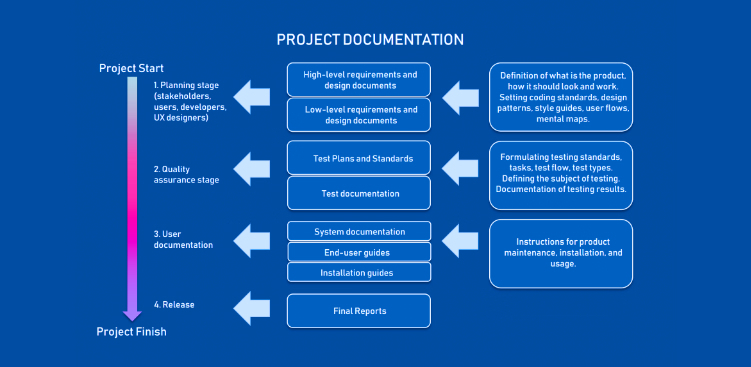
1. Define Clear Documentation Goals
Before diving into documentation, it’s crucial to define clear goals. Ask yourself what information needs to be documented and why?
Are you aiming to provide a historical record, facilitate collaboration, or ensure compliance with industry standards?
Having a clear purpose will guide your documentation efforts. To establish clear communication goals, it’s essential to define the purpose of your message. Outline what needs to be conveyed in the document i.e. project information, motivate stakeholders, educate teams, etc. It forms a well-defined purpose and sets the foundation for effective communication.
2. Establish Documentation Standards
The second step to document preparation is establishing documentation standards. It is important to keep the writing conventions and flow of ideas consistent while preparing the project documents.
Next the project managers need to identify the types of documents they need to create. Typically in a project development the common documents include user stories, product backlogs, sprint backlogs, release plans and sprint reviews.
3. Create a Project Documentation Plan
Develop a comprehensive documentation plan at the outset of the project. Outline what needs to be documented, who is responsible for each type of documentation, and when it should be created or updated. Having a plan in place helps prevent important details from slipping through the cracks.
The documentation plan outlines what needs to be documented, how it will be done, and when it should occur throughout the project’s lifecycle. This plan helps teams strike a balance between keeping records for compliance and knowledge preservation while avoiding unnecessary overhead.
4. Document Throughout the Project Lifecycle
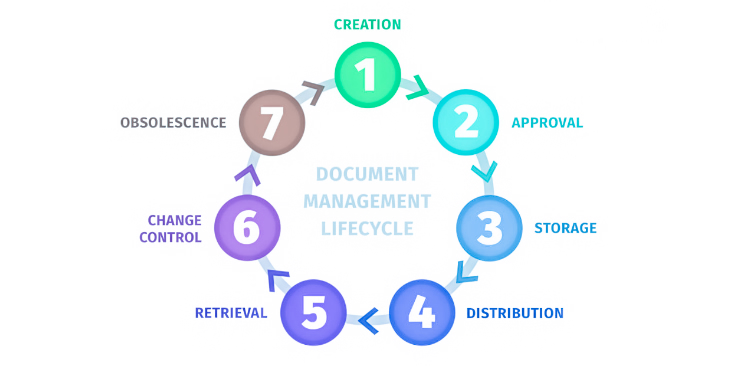
Effective project documentation isn’t a one-time effort. Document continuously throughout the project’s lifecycle. This includes planning documents, meeting minutes, status reports, change requests, and final deliverables.By documenting in real-time, you capture the most accurate and up-to-date information.
The creation of documents throughout a project’s life cycle involves several stages, each serving a specific purpose.
- Initially, during the project initiation phase, you start with a project charter that outlines the project’s purpose, scope, and key stakeholders.
- The planning phase involves creating documents like project plans, schedules, and budgets.
- During execution, work-related documents such as status reports, progress updates, and change requests documents are created.
- Monitoring and controlling phases involve risk assessments and issue logs.
- The project closure phase involves documents like final reports, lessons learned, and project summaries which are developed to capture the project’s outcomes.
Use collaboration tools like Orangescrum to streamline the documentation process. These tools come equipped with wiki management software that provides predefined templates and custom workflows for document preparation. These features simplify the creation and management of product documents.
5 benefits of using collaboration tools for documentation:
- Efficient Collaboration: Collaboration tools facilitate real-time collaboration among team members, regardless of their geographical locations.
- Version Control: Collaboration tools include version control features that track changes to documents.
- Centralised Access: With documents stored in a central, cloud-based location, authorised users can access files from anywhere with an internet connection
- Security and Permissions: Collaboration tools offer various security features, including user permissions and encryption, to protect sensitive data.
- Streamlined Workflow: These tools often integrate with project management and task tracking features, streamlining the workflow.
6. Maintain Version Control
Maintain a clear version control system for all project documents. Ensure that team members are using the most recent versions to avoid confusion and errors. Many document management systems offer version history tracking.
What are the benefits of version control?
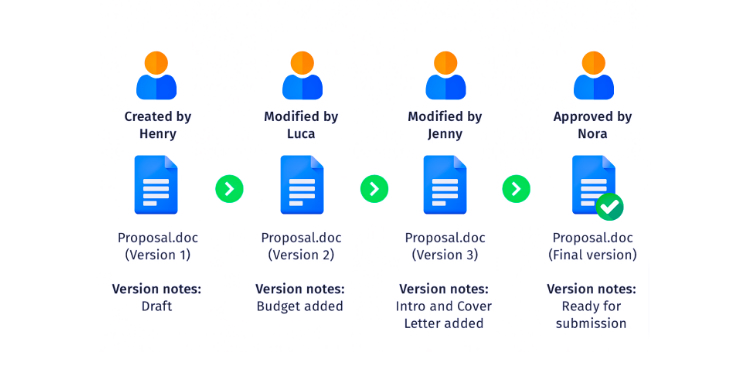
- Document history and tracking: Maintain a complete history of document changes. This enables data auditing, troubleshooting and accountability.
- Avoid data loss: Prevent data loss by pressing previous versions of the document. Avoid accidental data corruption by reverting to earlier, intact versions.
- Collaboration: Support concurrent collaboration on documents by multiple team members. Users can work on the same document simultaneously and manage merge conflicts.
- Traceability and compliance: It facilitates compliance by providing a documented change history which can be critical for audits and compliance with industry regulations.
- Save time and resources: Version control systems save time and resources that would otherwise be spent manually managing document versions, tracking changes, and resolving conflicts.
7. Keep It Concise and Relevant
Project managers should keep the documents concise and relevant. They should avoid unnecessary details and jargons. Instead, they should outline only the information that brings clarity to the project requirements.
Top Tips to Keep Project Documents Concise and Relevant
- Define Clear Objectives: Before creating any document, clearly define its purpose and objectives. Avoid including extraneous information that doesn’t directly contribute to the document’s goals.
- Use Clear and Concise Language: Opt for plain language and avoid overly complex or verbose sentences. Be straightforward in your communication, and use active voice to make the content more engaging and straightforward.
- Prioritize Information: Arrange the content in order of importance. Start with the most critical information and progressively move to less important details. This ensures that readers immediately grasp the key points.
- Security and Permissions: Instead of lengthy paragraphs, use bullet points or numbered lists to present information in a more organized and scannable format. Lists make it easier for readers to quickly absorb essential details.
- Visual Aids: Incorporate relevant visuals, such as diagrams, charts, and infographics, to illustrate complex concepts or data. Visuals can often convey information more efficiently than text.
- Regular Updates: Periodically review and update product documents to ensure they remain relevant. Information can become outdated quickly, and maintaining the document’s accuracy is essential.
- Keep an Executive Summary: Include an executive summary at the beginning of the document, providing a high-level overview for those who need a quick understanding without delving into the details.
8. Include Stakeholders
Involve stakeholders in the documentation process. Project managers should communicate to factor-in their perspectives while preparing their documents. This will ensure that the documents effectively reflect the project’s status and goals.
Top tips to consider when preparing documents for stakeholders:
- Understand Your Stakeholder: Begin by understanding your stakeholders’ needs, interests, and expectations. Tailor your document to address their specific concerns and priorities.
- Clear and Concise Content: Ensure that the document is clear, concise, and free of jargon. Use straightforward language and avoid unnecessary technical details that stakeholders may not understand.
- Executive Summary: Start with an executive summary that provides a high-level overview of the document’s key points. This summary allows busy stakeholders to quickly grasp the main takeaways.
- Structure and Formatting: Organize the document with a logical structure, including headings, subheadings, and bullet points. Use a consistent formatting style for a professional and easy-to-read appearance.
- Visuals and Graphics: Incorporate relevant visuals, such as charts, graphs, and infographics, to illustrate key data and trends. Visual aids can make complex information more accessible.
- Actionable Recommendations: If applicable, include actionable recommendations or next steps. Stakeholders appreciate documents that not only inform but also provide guidance on how to respond or make decisions based on the information presented.
- Review and Proofread: Carefully review and proofread the document to eliminate errors, typos, and inconsistencies. A well-edited document reflects professionalism and attention to detail.
- Meet Deadlines: Ensure that you meet deadlines for document delivery. Stakeholders rely on receiving information in a timely manner, so punctuality is crucial.
- Feedback and Iteration: After sharing the document, welcome feedback from stakeholders and be prepared to iterate and improve the document based on their input.
- Compliance and Legal Considerations: If the document has legal or compliance implications, make sure it adheres to relevant regulations and standards. Seek legal advice when necessary.
- Security and Confidentiality: Safeguard sensitive information and ensure that the document’s distribution complies with confidentiality requirements and data security protocols.
9. Review and Validate
More important than preparing documents is reviewing and validating the accuracy of the contents in it. It is advised to perform peer reviews and quality assurance processes to identify errors.
Top things to consider when reviewing and validating documents:
- Define Reviewers and Responsibilities: Identify the individuals or teams responsible for reviewing and validating the document. Assign specific roles and responsibilities to each reviewer, including subject matter experts, project managers, stakeholders, and quality assurance personnel.
- Establish Clear Criteria: Determine the criteria and standards against which the document will be evaluated. This could include project requirements, industry standards, organizational guidelines, and document-specific criteria such as clarity, consistency, and accuracy.
- Consolidate Feedback: Collect feedback and comments from all reviewers. Use a collaborative platform or document management system to centralize feedback and make it easily accessible to all stakeholders. Be sure to capture both positive aspects and areas that need improvement
- Hold a Review Meeting: Schedule a review meeting or discussion where the reviewers can share their feedback and discuss any discrepancies or differences in their assessments. Use this meeting to resolve conflicts and ensure a common understanding of the document’s quality.
- Document Revisions: After the review meeting, make necessary revisions to the document based on the feedback received. Ensure that the document aligns with the defined criteria and standards.
- Validate Content and Accuracy: Reviewers should validate the document’s content for accuracy, relevance, and completeness. Confirm that it addresses the project’s objectives and meets stakeholder expectations.
- Check Formatting and Style: Review the document for consistency in formatting, style, and language. Ensure that it adheres to the organization’s guidelines and is visually appealing and reader-friendly.
- Continuous Improvement: After the document is approved and in use, continue to monitor its effectiveness and collect feedback from users. Consider implementing changes or updates based on real-world usage and evolving project needs.
10. Archive and Retain
Effective project documentation doesn’t end when the project is completed. Archiving and retaining project documentation is a crucial best practice to preserve institutional knowledge and meet regulatory requirements.
By systematically storing and organizing project documents, you ensure that valuable information remains accessible for future reference, audits, or follow-up projects.
Proper archiving also safeguards against data loss and maintains a historical record of the project’s evolution and decision-making processes.
11. Provide Access and Training
To maximize the utility of project documentation, it’s essential to provide easy access to relevant stakeholders. This best practice involves setting up user-friendly document repositories or management systems that grant authorized individuals access to the right documents when they need them.
Additionally, offering training and guidance on how to navigate and utilize these resources ensures that team members and stakeholders can leverage project documentation effectively to support their tasks and decision-making processes.
One of the most valuable aspects of project documentation is the opportunity to learn from past projects. Effective project managers and teams continuously improve by reviewing past documentation to identify successes, challenges, and areas for enhancement.
By analyzing historical project documents, you can identify trends, best practices, and lessons learned that inform better decision-making, streamline processes, and ultimately lead to more successful future projects.
This best practice turns project documentation into a dynamic resource for ongoing improvement and innovation.
Conclusion
By implementing the best practices for project documentation, such as clear objectives, standardized templates, version control, and regular updates, organizations can streamline their project management processes and significantly reduce the risk of costly errors and miscommunications.
Whether you’re working on a small software development project or a large construction endeavour, the principles of effective project documentation apply across the board.
The key to successful project documentation is to keep it relevant, accessible, and up-to-date throughout the project’s lifecycle.
By making this a priority and integrating these best practices into your project management methodology, you’ll set your project up for success and contribute to a culture of efficiency and transparency within your organisation.
So, embrace the power of project documentation and watch as your projects thrive and your team’s productivity soars.